CDAC Science at the Z Fundamental Science Program Workshop
CDAC Academic Partner Steven Jacobsen (Northwestern University) presented a plenary lecture and graduate student Hannah Bausch presented a poster detailing her research at the recent Z Fundamental Science Program (ZFSP) Workshop, held August 6-9 in Albuquerque, NM, home of Sandia National Laboratories and Sandia’s Z Machine. The purpose of this annual workshop is to showcase recent shock compression work performed on Sandia’s Z machine within the ZFSP and to provide guidelines from Z facility personnel on the preparation of proposals for instrument time to carry out basic research in the area of dynamic compression with pulsed power sources.
Steve’s presentation was entitled “Origin of the Ultra-Low Velocity Zones Atop Earth’s Core-Mantle Boundary.” Hannah’s poster was entitled “Shock-Ramp Compression of (Mg,Fe)O up to Earth’s Core Conditions. CDAC-supported work at Northwestern employs Sandia’s Z machine with specially designed pulse sequences and unique experimental configurations to reach thermodynamic states that are not accessible with either static compression or other dynamic compression methods. Steve’s and Hannah’s work addresses the properties and evolution of complex structures at Earth’s core-mantle boundary region that have been observed through anomalies in seismic data.
For more on the ZFSP and to view the workshop agenda, see the workshop website.
========================================================================================
Compression of Planetary Gas Mixtures : The Hydrogen-Helium System
Developing equations of state (EOS) for mixtures of gases presents a variety of technical challenges arising from the differences in the physical properties of the components. In the case of the H2-He system, despite the apparent chemical simplicity of these two-electron systems, the behavior of their mixtures is complicated by nonideal mixing and phase transitions in H2 at high pressures.
In new work carried out through a collaboration between Sandia National Laboratories and UIC, accurate pressure-density EOS for hydrogen-helium mixures have been determined to 44 GPa, representing greater than fourfold compression. Data obtained using both hypervelocity gas guns and Sandia’s Z machine on precompressed samples, in combination with Brillouin spectroscopy on samples under pressure in the diamond anvil cell,1 have resulted in equations of state for H2-He mixtures with less than 10% uncertainty in the density (Fig. 1). This allows discrimination between various possible equation of state models for H2-He mixtures as well as the benchmarking of proposed planetary models. This work has important implications for understanding the dynamics of gas giant planets and their satellites, as well as the development of experimental techniques on shock compression platforms.
The lead author on this work is Sakun Duwal, a former CDAC graduate student and now a Principal Technical Staff Member in the Dynamic Material Properties (DMP) Department at Sandia National Laboratories. The DMP research program is led by Chris Seagle, also a former CDAC graduate student, from the University of Chicago.
1 Zoller, C. M., M. Ahart, S. Duwal, R. C. Clay III, C. T. Seagle, Y. J. Ryu, S. Tkachev, S. Chariton, V. Prakapenka, and R. J. Hemley, Accurate equation of state of H2-He binary mixtures up to 5.4 GPa. Physical Review B 108, 224112 (2023).
_____________________________________________
Duwal, S., R. C. Clay III, M. D. Knudson, J. Boerner, K. Cochrane, J. Usher, D. Dolan, B. Farfan, C. de La Cruz, J. Banasek, C. T. Seagle, R. Hacking, S. Payne, C. Zoller, M. Ahart, and R. J. Hemley, Extreme compression of planetary gases: High-accuracy pressure-density measurements of hydrogen-helium mixtures above fourfold compression. Physical Review B, 109, 104102 (2024).
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the APS March Meeting 2024

CDAC scientists presented an array of discoveries in condensed matter physics, from superconductivity to energetic materials and quantum matter, at the 2024 American Physical Society March Meeting, held March 4-8 in Minneapolis, MN. The meeting included eight presentations involving CDAC students, postdocs, research staff, faculty and collaborators. CDAC personnel contributed to a variety of technical sessions, and addressed the Thermomechanical Extremes and Chemical and Material Extremes thrusts in the CDAC scientific program.
CDAC Director Russell Hemley gave an invited presentation, “Toward Ambient Superconductivity” in the session on Frontiers in Static and Dynamic Compression of Condensed Matter. CDAC academic partner Eva Zurek is chair-elect of the APS Division of Computational Physics and helped organize this as well as a number of other sessions at the meeting related to theoretical and computational approaches.
CDAC academic partner Steve Jacobsen and graduate student Hannah Bausch (Northwestern) were a co-authors on the presentation, “Combined Self-Consistent DFT+U and Quantum Monte Carlo Investigation of the High Pressure Spin Transition in Ferropericlase” (Abstract N20.00005), presented by Joshua Townsend, a former CDAC graduate student at Northwestern and currently a staff scientist at Sandia National Laboratories.
Adam Denchfield (UIC) Candidate High-Tc Superconductors in a Class of Quaternary Hydrides
Co-Authors : R.J. Hemley, H. Park
(Abstract N15.00004)
Husam Farraj (UIC). Structural Phase Transitions in KC8 under High Pressure
Co-Authors : R.J. Hemley, J. Cabana, M. Aihaiti, H.P. Liermann, K. Glazyrin, Y. Meng
(Abstract G20.00007)
Clayton Halbert (UIC). High-Pressure Structure, Equation of State, and superconductivity of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3: Observation of a Novel Bi-Sb-Te Alloy
Co-Authors: N.P. Salke, L. Deng, S. Song, X. Shi, Z. Ren, C.W Chu, R.J. Hemley
(Abstract G20.00002)
Russell Hemley (UIC, Invited). Toward Ambient Superconductivity
(Abstract B45.00002)
Alexander Mark (UIC). Phase Sensitive Detection Applied to Superconducting Transport Measurements
Co-Authors: N.P. Salke, M. Ahart, R.J.Hemley
(Abstract G20.00004)
Roma Ripani (UIC). Vibrational Dynamics of Hydrazine to 50 GPa
Co-Authors: F. Safari, Z. Liu, M. Aihaiti, S.A. Gramsch, R.J. Hemley
(Abstract M20.00012)
Nilesh Salke (UIC). Electrical Resistance and Magnetic Susceptibility Evidence for Near Ambient Superconductivity in Nitrogen-Doped Lutetium Hydride
Co-Authors: A.C. Mark, M. Ahart, R.J. Hemley
(Abstract G20.00006)
Eva Zurek (Buffalo). Theoretical Design of Light-Element Superconductors
(Abstract F20.00002)
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the 2024 SSAP Symposium

CDAC science was once again well represented this year at the annual Stewardship Science Academic Programs (SSAP) Symposium, which was held in Arlington, Virginia on February 21-22, 2024. Students from UIC and all six CDAC academic partner groups presented posters on their research, and CDAC Director Russell Hemley gave an overview of the Center’s current progress and a preview of the next phase of CDAC, which is set to begin on July 1, 2024.
The SSAP Symposium brings together representatives from DOE/NNSA-sponsored Centers of Excellence and individual grant holders in the areas of Materials at Extreme Conditions, Low Energy Nuclear Science, and High Energy Density Physics. At one time the only Center devoted to the study of materials in extreme conditions, CDAC is now joined by several other materials centers with a diversity of scientific programs and research approaches. Students from across the SSAP also had an opportunity to network with representatives from the NNSA laboratories to explore future postdoctoral opportunities.
Keynote speaker David Hoaglund, Executive Principal Assistant Deputy Administrator for Defense Programs within DOE/NNSA, outlined some of the important implications for the field of stewardship science in an increasingly unpredictable geopolitical landscape. In his address, Mr. Hoagland drew attention to the key contributions to international security that are provided by a robust commitment to scientific research and development in this field. The full agenda for the symposium is available at the SSAP Symposium website.
CDAC students attending the SSAP Symposium this year, along with their poster titles are as follows:
Hannah Bausch (Northwestern) : Shock-Ramp Compression of (Mg,Fe)O up to Earth’s Core Conditions
Co-Authors : J. P. Townsend, S. Duwal, C. A. McCoy, J.-P. Davis, T. Abbott, A. N. Clark, S. D. Jacobsen
Audrey Berlin (Utah) : High Pressure Effects of Light Elements on Fe50Ni50 Plasticity
Co-Authors : E. E. Ledoux, C. Kiessner, L. Miyagi
Brian Blankenau (UIUC) : Magnetostructural Phase Transformations in Ni50 Mn50-x Inx Shape Memory Alloys
Co-Authors : T. Su, R. Kumar, D. Popov, E. Ertekin
Husam Farraj (UIC): Study of a Novel Cathode Material by Raman Scattering, and X-ray and Neutron Diffraction Under Various P-T Conditions
Co-Authors: N. Sunariwal, I. Roy, J. Hirtz, R. Kumar, M. Diamond, M. Ahart, M. Lang, J. Cabana, R. Hemley
Clayton Halbert (UIC) : High-Pressure Structure and Equation of State of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3:Observation of Superconductivity in a Novel Bi-Sb-Te Alloy
Co-Authors: N. Salke, A. Manayil-Marathamkottil, H. Farraj, M. Ahart, L. Deng, C. Chu, S. Song, X. Shi, Z. Ren, H. Liermann, Y. Meng, K. Glazyrin, R. Hemley
Masashi Kimura (Buffalo) High-Pressure Searches of Ternary YCaHn Systems
Co-Author: E. Zurek
Jacob Minnette (Tennessee) : Coupled Extremes in Nuclear Materials
Co-Authors: J. Hirtz, W. Cureton, C. Park, I. Schubert, I.Ivanov, A. Berlin, C. Kiessner, L. Miyagi, M. Lang.
Allison Pease (Michigan State) : Liquid Structure of Iron-Nitrogen-Carbon Alloys Within the Cores of Small Terrestrial Bodies
Co-Authors : J. Liu, J. Piper, M. Lv, Y. Kono, S. Dorfman
Morgan Reddington (Buffalo) : Tritium Adsorption and Transfer on Pure and Tin Defective Zirconium
Co-Authors: H. P. Paudel, E. Zurek, D. N.Tafen, Y. Duan
Roma Ripani (UIC) : Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction, Raman and Infrared Study of Hydrazine to 50 GPa
Co-Authors : F. Safari, S. Gramsch, M. Ahart, Z. Liu, R. Hemley
Charlie Zoller (UIC) : Optical Properties of Aluminum Under Pressure and Temperature
Co-Authors : S. Duwal, Z. Liu, R. Clay, S. Chaudhuri, D. Dolan, C. Seagle, R. Hemley
========================================================================================
Fundamentals of Quantum Materials Winter School and Workshop 2024

The 7th annual FQM school focused on High Pressure Synthesis and Measurement, areas of research of great interest to CDAC. As a result, CDAC made a strong showing at the school and accompanying workshop.
CDAC Students Abdul Haseeb Manayil Marathamkottil, Eduardo Poldi, Husam Farraj and Roma Ripani attended the event while CDAC’s director Russell Hemley contributed to the Workshop Program by presenting a talk entitled ‘Progress on High Tc Hydride Superconductivity.’
FQM 2024 targeted students who are starting to work with either high pressure experiments or sample growth and included a combination of fundamental materials synthesis instruction as well as lectures on experimental techniques and practice from invited speakers with diverse expertise.
The school covered diamond anvil cell techniques in a practical way, with a focus on various types of DAC measurements available at universities as well as synchrotron and neutron facilitiess. Discussion sessions engaged students and other early early career scientists on topics of current interest.
The Workshop on the final day featured a series of lectures that highlighted topics at the
forefront of quantum materials under pressure.
See FQM’s website for more information
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the AGU Fall Meeting 2023
CDAC was well represented at the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting held in San Francisco, CA from December 11-15. Four graduate students and one CDAC faculty partner presented their CDAC-supported research focused on the behavior of materials at extreme conditions, highlighting topics in both the Thermomechanical Extremes and Chemical and Material Extremes thrust areas of the CDAC scientific program.
Graduate students from several CDAC groups pursue research on Earth and planetary materials. The complex, often multi-phase and non-stoichiometric nature of these materials provides a rich training ground for developing an understanding of material behavior in extreme conditions.
Hannah Bausch (Northwestern) presented a poster outlining her work on the shock-ramp compression of (Mg,Fe)O on Sandia’s Z machine, and was also a co-author on Luisa Chavarria’s (Michigan State) poster presentation on the incorporation of sodium into (Mg,Fe)O at lower mantle conditions.
Allison Pease (Michigan State) presented a poster on the thermal equation of state of transition metal-bearing CaSiO3 and its implications for large, low shear velocity zones in the lower mantle, and Audrey Berlin (Utah) gave an oral presentation on the contributions of light elements, pressure, temperature and strain on the formation of the L10 FeNi alloy in a session on iron and iron-bearing phases in planetary interiors.
CDAC Academic Partner Lowell Miyagi (Utah) also gave a poster on the recent development of a novel dynamic diamond anvil cell for high strain rate measurements during radial diffraction measurements. This work is part of a collaboration with the Materials Physics and Applications Group at LANL headed by Blake Sturtevant.
========================================================================================
Multi-Stage Defect Accumulation in Zirconium Carbide Under Irradiation
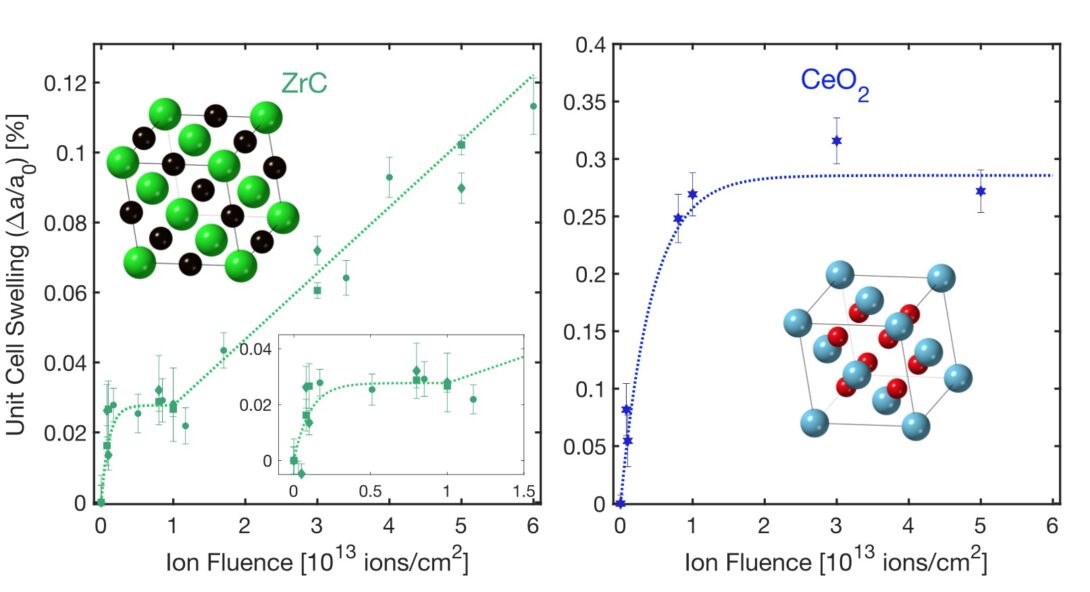
Microcrystalline zirconium carbide exhibits lattice expansion due to defect accumulation in two distinct regimes, which differs from the behavior of oxide materials such as CeO2. This contrasting behavior is observed across different grain sizes.
CDAC graduate student Jacob Minnette, from the group of Academic Partner Maik Lang at the University of Tennessee, along with collaborators from the Lang group, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, HPCAT, and the GSI Helmholzzentrum and the Technische Universität in Darmstadt, Germany, have published the results of important new work on the behavior of zirconium carbide under heavy ion irradiation. This paper is highlighted on the cover of the issue of the Journal of Applied Physics in which it appears.
Zirconium carbide (ZrC) is a material that falls within the broader classification of ultra-high temperature ceramic (UHTC) compounds. These materials possess thermomechanical properties that are of interest for a wide variety of emerging energy and aerospace technologies, which often have operating conditions characterized by extreme conditions. In this work, ZrC was studied with synchrotron X-ray diffraction after exposure to energetic heavy ions. Investigations of materials under such intensely ionizing radiation enables a glimpse of their behavior in conditions far from thermodynamic equilibrium.
The effect of irradiation on such ceramic materials is typically concentrated within small point-like defects that lead to crystal lattice swelling and the accumulation of strain, which reaches a saturation limit above a critical ion fluence. In ZrC exposed to 946 MeV Au ions, an unexpected and complex multi-stage defect accumulation trend comprising of initially rapid lattice swelling takes place, followed by saturation, before a secondary linear swelling regime is observed. Lattice swelling then continues to increase linearly under irradiation up to the highest fluence evaluated in this study, 6×1013 ions/cm2.
The origin of this behavior likely originates from the hypostoichiometric nature of ZrC, which is typical of many UHTC compounds. This swelling mechanism was consistently observed for samples prepared with different synthesis methods and is distinct from what is observed with cerium dioxide irradiated under identical conditions (Fig. 1). This study highlights the fact that materials can respond very differently to extreme environments, and that studying defect accumulation under energetic heavy ion irradiation is an important step in the development of more robust materials for energy-related applications.
Minnette, J., E. Williams, W. Cureton, A. Solomon, E. O’Quinn, M. Kurley, R. D. Hunt, C. Park, I. Schubert, C. Trautmann, and M. Lang, Response of ZrC to swift heavy ion irradiation. Journal of Applied Physics, 134, 185901 (2023).
========================================================================================
CDAC at Z : Participation at the 2023 Z Fundamental Science Program Workshop
The 14th Z Fundamental Science Program (ZFSP) Workshop Fundamental Science with Pulsed Power was hosted by Sandia National Laboratories at the Hotel Analuz in Albuquerque, NM on August 9-11, 2023. CDAC was represented by Academic Partner Steven Jacobsen and graduate student Hannah Bausch from Northwestern University, and graduate student Charlie Zoller from UIC.
Jacobsen gave a plenary talk titled “Origin of the Ultra-Low Velocity Zones Atop Earth’s Core-Mantle Boundary,” which outlined recent progress following a series of shots at Z carried out as part of Hannah Bausch’s PhD research. She also presented a poster at the Workshop, “Shock-Ramp Compression of (Mg,Fe)O up to Earth’s Core Conditions.” Zoller’s presentation, “Aluminum Reflectance Measurements Using the Diamond Anvil Cell,” reported results obtained at the Frontier Infrared Spectroscopy beamline at the National Synchrotron Light Source, Brookhaven National Laboratory.
The goal of the ZFSP Workshop is to provide an opportunity for current and prospective users at Z to to discuss research directions and formulate new ideas for collaborative work on Z. Research directions currently supported by the ZFSP research areas are Astrophysics, Planetary Science, Materials Physics, and Magnetized High Energy Density Science relevant to Magnetized Inertial Fusion.
The scientific program and details on presentations for the breakout sessions are available on the workshop website.
========================================================================================
CDAC at SCCM 2023

CDAC was pleased to contribute to the 23rd Biennial Conference of the American Physical Society Topical Group on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter (SCCM), which was held in Chicago June 18-23, 2023.
Of the Technical Focus Areas in the program, two Focus Areas were devoted to research in static compression of materials.
CDAC Partners Dana Dlott and Steven Jacobsen contributed abstracts to the meeting, and CDAC graduate student Hannah Bausch (Northwestern) also made a presentation detailing her studies on the shock-ramp compression of (Mg,Fe)O. Charlie Zoller, a CDAC graduate student from UIC, presented a poster on his work in developing an equation of state for H2-He mixtures. HPCAT staff and users also made seven presentations across a range of Focus Areas.
Santanu Chaudhuri, a CDAC-affilliated faculty member from UIC also presented two talks describing his computational work on energetic materials.
CDAC Deputy Director Stephen Gramsch served on the Technical Committee for the Static Compression sessions. Current HPCAT Group Leader and former CDAC Research Scientist Maddury Somayazulu chaired the session on New Materials and Equations of State, and CDAC Research Scientist Ravhi Kumar chaired a session on Simulations and Phase Transitions.
Highlighting the meeting was the plenary session during which the first Neil W. Ashcroft Early Career Award was presented to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s Richard Kraus, a CDAC collaborator. The plenary lecture, “Pressing On, Regardless: Scientific Impacts of Neil W. Ashcroft” was presented by CDAC Director Russell Hemley (Fig. 1) and traced some of the many fundamental scientific contributions that the late Professor Ashcroft made throughout his illustrious career at Cornell University. Ashcroft was also a long-time member of the CDAC Center Scientific Advisory Committee.
Link to the SCCM23 Scientific Program
Links to CDAC and HPCAT Presentations
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the APS March Meeting 2023

The 2023 American Physical Society March Meeting took place as an-person event, with some virtual sessions also included, from March 5-10 in Las Vegas, NV. CDAC once again made a strong showing at the meeting with 20 presentations made by CDAC students, postdocs, research staff, faculty, and collaborators.
Six UIC graduate students : Husam Faraj, Abdul Haseeb, Alexander Mark, Roma Ripani, Charles Zoller, (oral) and Amol Lamichhane (poster) presented the results of their recent work, while two UIC undergraduates, Cade Vallero and Jonathan Simon, both gave oral presentations for the second consecutive year. Brian Blankenau, from the group of CDAC Partner Elif Ertekin at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign also presented his work in a virtual session.
The breadth CDAC scientific program was well represented at the March Meeting this year, with contributions documenting progress in the Elasticity and Equations of State, Complex Materials, Extreme Chemistry, Phase Transition Dynamics, and Superconductivity/Electronic and Magnetic Materials Thrusts.
========================================================================================
Chemical Interactions That Govern the Structures of Metals
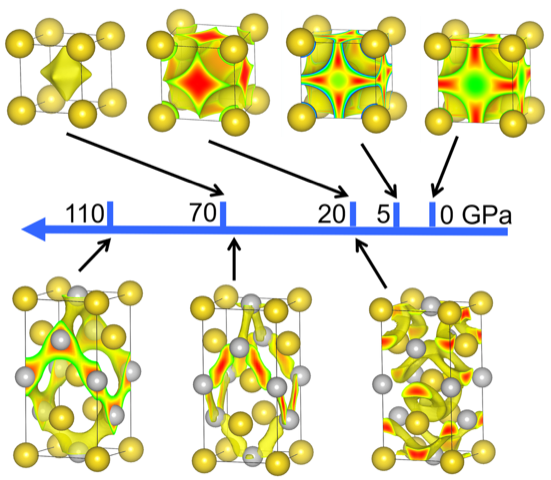
What determines the structures of simple metals has been a subject of a longstanding debate among researchers, and findings from a new study appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences add new information to consider in the discussion.
By analyzing the electronic properties of metals in various lattices over a broad range of sizes and geometries, CDAC Director Russell Hemley and collaborators shifted from a “physics” band-structure point of view to a “chemical” perspective to find highly complex structures that emerge at high pressures in these materials. This has led to a new theory that can explain why a particular structure is favored for almost all metals in the periodic table.
“This theory is based on our finding that the electrons in many metals occupy what we call quasi-atom orbitals — the local quantum orbitals centered at the voids between the atoms. In large measure, it is the chemical interactions between localized electrons that control the structure of the metals,” Hemley said.
The result contrasts with the traditional view that structures and other properties are determined by the extended electronic states, which behave close to what is known as a free electron gas. However, the structure preference of classes of metals across the periodic table cannot be explained by this “physics,” or band structure point of view.
One reason the research team is particularly excited about this work is that the idea originated from the need for a simple “chemical’ explanation for the existence of high-pressure electrides, a surprising phenomenon that includes for example the fact that some alkali metals become transparent insulators under pressure. The findings have implications for the behavior of chemically complex materials, including alloys, intermetallics, hydrides, ionic compounds and two-dimensional materials.
“This is an example of how the study of matter under extreme conditions can inform us about chemistry and materials under normal, or more familiar conditions. Thus studies of materials at high pressure can reveal chemical features that might be otherwise neglected,” Hemley said.
Sun, Y., L. Zhao, C. J. Pickard, R. J. Hemley, Y. Zheng, and M. Miao, Chemical interactions that govern the structures of metals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 120, e2218405120 (2023).
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the 2023 SSAP Symposium
For the first time since 2020, the annual Stewardship Science Academic Programs (SSAP) Symposium took place in person, this year at the Buffalo Thunder Resort in Santa Fe, NM on February 14-15. This year’s meeting represented a welcome return to the lively interpersonal interactions between faculty, students and NNSA laboratory scientists that have been a hallmark of the SSAP Symposium since the inception of the program in 2003. Over 300 graduate students from across the collection of SSAP Centers and groups of SSAP grant holders were in attendance and presented posters detailing progress on their studies, making this the largest SSAP Symposium to date.
Dr. Ellen Cerreta, Associate Laboratory Director for Physical Sciences at Los Alamos National Laboratory, presented the keynote address, “An Exciting Time for a Career at an NNSA Lab,” providing an overview of emerging opportunities for postdoctoral researchers and scientific and engineering staff, as the mission space for the NNSA laboratories continues to grow.
In addition, representatives from each of the NNSA laboratories and the Kansas City and Nevada National Security facilities presented overviews of the wide variety of research activities underway at their locations. Personnel from each facility were also available to discuss with students individually the many opportunities available for students finishing graduate work and looking to continue their training within the NNSA complex.
SSAP grant holders and a selection of SSAP Center directors provided updates on progress in their programs in the Materials, High Energy Density Physics, and Low Energy Nuclear Science sections.
Nine CDAC students presented posters on their research, with Allison Pease, a student from the group of Academic Partner Susannah Dorfman at Michigan State University, receiving a Best Poster Award. The CDAC students attending the meeting and their poster titles are:
Hannah Bausch, Northwestern University
Shock-Ramp Compression of Iron-Rich (Mg,Fe)O up to Earth’s Core Conditions
Brian Blankenau, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Exploring Pressure and Temperature Induced Manetostructural Phase Transitions in Ni2Mn2-xInx Alloys
Chantelle Kiessner, University of Utah
Texture Development and Strength of Irradiated Ceria
Alexander Mark, University of Illinois Chicago
Probing the Anomalous Changes in Structural and Electronic Properties of Bi2Sr2Can-1CunO2n+4+δ to Megabar Pressures
Jacob Minnette, University of Tennessee
Nuclear Fuel Type Materials Under Extreme Conditions
Allison Pease, Michigan State University
Fe-Nitride Spin Transition Under Nonhydrostatic Compression and Impacts on the Strength of Fe-Nitrides
Roma Ripani, University of Illinois Chicago
Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction, Raman and Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrazine at High Pressure
Zachary Whipple, University of Illinois Chicago
Compression of a Triamine High Energy Density Material
Charles Zoller, University of Illinois Chicago
Accurate Equation of State of Fluid H2-He Mixtures
Next year’s SSAP Symposium will take place in the Washington, DC area in February 2024.
========================================================================================
Rare Earth Phosphates : Diverse Structures, Similar Irradiation Response
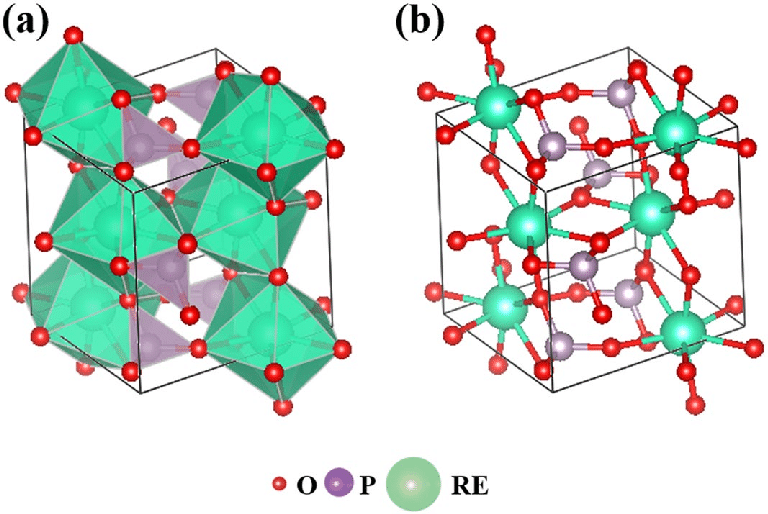
Diverse structure types for rare earth element phosphates yield similar amorphization behavior under ion irradiation, despite very different structures and responses to compression.
Rare earth element (REE) phosphates are an attractive host material for the long-lived decay products found in spent nuclear fuel due to their high radiation tolerance. REE phosphates adopt different structure types (Fig. 1) depending on the size of the rare earth element — lighter, larger rare earth ions are stable in the monoclinic monazite structure, while heavier, smaller rare earth ions prefer the tetragonal xenotime structure. Results from X-ray diffraction studies at high pressure show that these different structure types respond very differently to compression, which raised the possibility that their behavior under irradiation by energetic heavy ions would also be distinct.
Using one of the world’s largest ion accelerators at the Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research (Darmstadt, Germany), a group including CDAC Academic Partner Maik Lang, former CDAC students Will Cureton and Raul Palomares, and current student Cale Overstreet, along with colleagues from the Institute of Energy and Climate Research (Jülich, Germany), the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (Karlsruhe, Germany), and Stanford University have studied the response of SmPO4 (monazite structure) and TbPO4 (xenotime structure) under intense heavy ion irradiation. The work aims to model how robust these structures are in response to intense radiation and to evaluate their potential stability in a nuclear waste storage environment.
Transmission electron microscopy shows that both materials lose crystallinity under irradiation in a very similar manner, experiencing some degree of amorphization. The local structural arrangement within the amorphous region is also retained in both materials as confirmed by Raman spectroscopy, suggesting that, despite their different structures, changes in chemistry that might take place within nuclear waste forms will not dramatically affect these materials’ responses to ion irradiation.
Overstreet, C., J. Cooper, E. O’Quinn, W. Cureton, R. Palomares, J. Leys, G. Deissmann, S. Neumeier, C.-H. Chen and M. Lang, Structural stability of REE-PO4 (REE = Sm, Tb) under swift heavy ion irradiation. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 527, 34-39 (2022).
========================================================================================
Ultrahard Diboride Superconducts Under Pressure
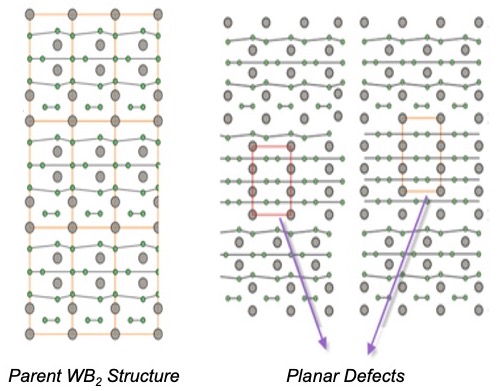
A unique combination of high-pressure structural studies and transport experiments, together with structure simulations, has led to the discovery that the ultrahard boride WB2 becomes a superconductor under pressure.
Ultrahard materials exhibiting high temperature superconductivity could have many important technological applications, including the fabrication of wear resistant abrasive devices, micro-electro-mechanical systems, and power engineering. Two decades of research on possible high Tc superconductors in members of the diboride family of compounds other than MgB2, however, have not resulted in any materials exhibiting high Tc superconductivity. Now, a CDAC collaboration including the UIC group, the groups of James Hamlin at the University of Florida, and former CDAC partner Yogesh Vohra at the University of Alabama-Birmingham, and the HPCAT team at the Advanced Photon Source, reports that superconductivity emerges in ultrahard WB2 at extreme conditions.
The abrupt appearance of superconductivity at 55 GPa (with a maximum Tc of 17 K at 91 GPa) does not coincide with any drastic structural change but instead is associated with the formation and percolation of mechanically induced stacking faults and twin boundaries in the parent structure under plastic deformation (Fig. 1). This unprecedented creation of superconductivity through mechanically induced metastable defects opens up new opportunities to search for other materials systems in which metastable structures can be stabilized in the form of planar defects. The use of extreme conditions therefore provides a new route for designing ultrahard superconductors at ambient pressure through defect microstructures that result in novel material properties.
Lim, A. C. Hire, Y. Quan, J. S. Kim, S. R. Xie, S. Sinha, R. S. Kumar, D. Popov, C. Park, R. J. Hemley, Y. K. Vohra, J. J. Hamlin, R. G. Hennig, P. J. Hirschfeld, and G. R. Stewart, Creating superconductivity in WB2 through pressure-induced metastable planar defects. Nature Communications 13, 7901 (2022).
========================================================================================
Exotic Crystal Chemistry at Extremes
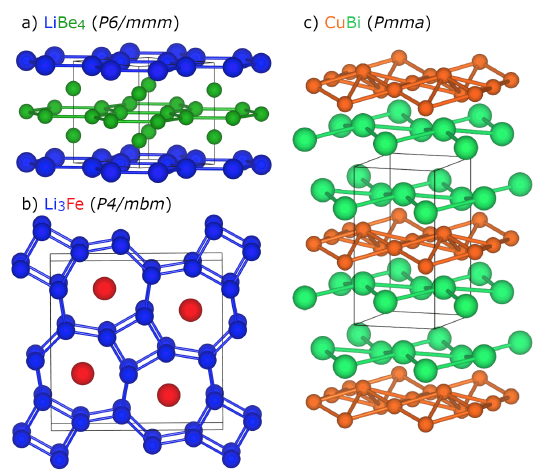
Although most of chemistry as we experience it commonly takes at close to 1 atmosphere, the range of pressure in the universe actually covers an incredible range, from the near-zero pressures of interstellar space to the centers of neutron stars. With advances in the technology of high pressure devices, and the development of new analytical methods for investigating matter at high pressures, the extreme conditions research community continues to uncover new examples of the surprising effects of applied pressures far away from our familiar 1 atmosphere environment.
In a new review article, CDAC Postdoc Katie Hilleke and CDAC Partner Eva Zurek highlight some of the surprising effects of high pressure, typically up to the 200-300 gigapscal (2-3 million atmospheres) range, on structure and bonding in a wide variety of materials. Starting with the ways in which pressure modifies atomic energy levels on compression, the authors proceed to discuss the response of crystals to applied pressure, both in terms of overall crystallographic structure and how this is related to changes in the overall electronic structure of the solid.
With this background, the authors describe a variety of materials where applied pressure produces truly novel behavior, including high pressure electrides, solid compounds that contain electrons that play the role of negatively charged ions, and noble gas compounds such as Na2He and related materials that only form at pressures sufficient to allow the “inert” He atom to react. Unexpected chemical compositions, such as those shown in Fig. 1 that are predicted or observed to become stable only at high pressures, and unusual bonding motifs that emerge in elemental materials such as boron, attest to the rich array of structure and bonding systematics yet to be explored and developed with emerging computational and experimental methods. Hilleke and Zurek also highlight the surprising effects of pressure on superconductivity in hydrogen and other elements, as well as hydrides in both clathrate-like and covalent systems.
[1] Feng, J., R. G. Hennig, N. W. Ashcroft, and R. Hoffmann, Emergent reduction of electronic state dimension in dense ordered Li-Be alloys. Nature 451, 445-448 (2008).
[2] Zhou, Y., Q. Xu, C. Zhu, Q. Li, H. Liu, H. Wang, and J. S. Tse, Predicted lithium-iron compounds under high pressure. RSC Advances 6, 66721-66728 (2016).
[3] Guo, K., L. Akselrud, M. Bobnar, U. Burkhardt, M. Schmidt, J.-T Zhao, U. Schwarz, and Y. Grin, Weak interactions under pressure: hp-CuBi and its analogues. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 56, 5620-5624 (2017).
[4] Clarke, S., M. Amsler, J. P. S. Walsh, T. Yu, Y. Wang, Y. Meng, S. Jacobsen, C. Wolverton, and D. E. Freedman, Creating binary Cu-Bi compounds via high-pressure synthesis: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Chemistry of Materials 29, 5276-5285 (2017).
Hilleke, K. P. and E. Zurek, Crystal chemistry at high pressure. Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering: Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry III ; DOI:10.1016/B978-0-12-823144-9.00170-9. Elsevier, 2022.
========================================================================================
CDAC Classics -- Top 10 Papers by Citation Number

The Center is pleased to report that as of September 1st, 2022, the following papers have been cited 5,563 times since CDAC was founded in 2003:
- Ahart, M., M. Somayazulu, P. Dera, H.-k. Mao, R. E. Cohen, R. J. Hemley, R. Yang, H. P. Liermann, and Z. Wu, Origin of morphotropic phase boundaries in ferroelectrics. Nature 451, 545-548 (2008). —839 citations.
- Somayazulu, M., M. Ahart, A. K. Mishra, Z. M. Geballe, M. Baldini, Y. Meng, V. V. Struzhkin and R. J. Hemley, Evidence for Superconductivity Above 260 K in Lanthanum Superhydride at Megabar Pressures. Physical Review Letters 122, 027001 (2019). —823 citations.
- Mao, W. L., H.-k. Mao, P. Eng, T. P. Trainor, M. Newville, C. C. Kao, D. Heinz, J. Shu, Y. Meng and R. J. Hemley, Bonding changes in compressed superhard graphite. Science 302, 425-427 (2003). —653 citations.
- Li, Q., Y. Ma, A. R. Oganov, H. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Xu, T. Cui, H.-k. Mao, and G. Zhou, Superhard monoclinic polymorph of carbon. Physical Review Letters 102, 175506 (2009). —561 citations.
- Gregoryanz, E., C. Sanloup, M. Somayazulu, J. Badro, G. Fiquet, H.-k. Mao and R. J. Hemley, Synthesis and characterization of a binary noble metal nitride. Nature Materials 3, 294-297 (2004). —550 citations.
- Young, A. F., C. Sanloup, E. Gregoryanz, S. Scandolo, R. J. Hemley and H.-k. Mao, Synthesis of novel transition metal nitrides IrN2 and OsN2. Physical Review Letters 96, 155501 (2006). —543 citations.
- Liu, H., I. I. Naumov, R. Hoffmann, N. W. Ashcroft, and R. J. Hemley, Potential high-Tc superconducting lanthanum and yttrium hydrides at high pressure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 114, 1704505114 (2017). —530 citations.
- Angel, R., M. Bijak, J. Zhao, G. D. Gatta, and S. D. Jacobsen, Effective hydrostatic limits of pressure media for high-pressure crystallographic studies. Journal of Applied Crystallography 40, 26-32 (2007). —506 citations.
- Zhang, W., A. R. Oganov, A. F. Goncharov, Q. Zhu, S. E. Boulfelfel, A. O. Lyakhov, E. Stavrou, M. Somayazulu, V. B. Prakapenka, and Z. Konôpková, Unexpected stable stoichiometries of sodium chlorides. Science 342, 1502-1505 (2013). —433 citations.
- Struzhkin, V. V., B. Militzer, W. L. Mao, H.-k. Mao and R. J. Hemley, Hydrogen storage in clathrates. Chemical Reviews 107, 4133-4151 (2007). —402 citations.
Altogether over 1700 papers have been published as a direct result of CDAC funding. View all of them here.
========================================================================================
Shapeshifting Atoms Inside Earth
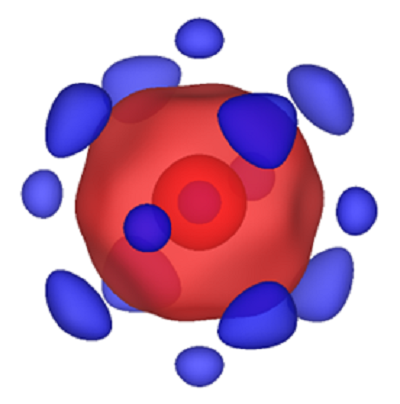
Atoms are commonly thought of as being round. New experiments by a CDAC-funded team from UC Berkeley and Northwestern University, together with scientists atand Argonne National Laboratory, report that pressure causes iron atoms to change shape deep inside our planet, however. This shapeshift alters the physical and chemical properties of crystals at depth, influencing the way Earth has evolved over its multi-billion-year history.
The high pressures of Earth’s interior can be reproduced in laboratory experiments that squeeze minerals samples between the tips of two diamonds. Previous experiments have shown that the electron clouds making up iron atoms within minerals collapse under less than a million times atmospheric pressure, conditions at roughly one quarter the depth toward our planet’s center. Dubbed an electronic spin transition, the change affects the electrons involved in chemical bonding between iron and other atoms, as well as the shape of the atoms.
This change in shape of the iron atoms has now been directly imaged for the first time at high-pressure, using high-intensity x rays from the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory. In their collapsed form, the iron atoms look like cubes with the corners cut off, and this affects how light, heat, and sound are transmitted through crystals containing iron.
Seismic waves from distant earthquakes are used to illuminate Earth’s interior, just as ultrasound is used for imaging the human body in medicine. High-pressure laboratory measurements are crucial for interpreting these seismic images and understanding the processes by which the interior cools over geological time.
Beyond imaging the shapes of atoms, the new measurements provide direct tests – means for improvements – of modern quantum simulations because the distribution of electrons within crystals is among the prime results obtained from atomistic theory. Quantum theory is widely used to develop new materials for society.
Atomic imaging at deep-Earth pressures is now a reality that can be used in basic science as well as applied technology.
The work was led by CDAC-funded graduate student, Matthew Diamond – now a postdoc at University of Illinois Chicago – as part of his Ph.D. thesis at UC Berkeley.
Diamond, M. R., G. Shen, D. Y. Popov, C. Park, S. D. Jacobsen, and R. Jeanloz, Electron Density Changes across the Pressure-Induced Iron Spin Transition. Physical Review Letters 129, 025701 (2022).
========================================================================================
Ahead of the Curve on Extreme Stress

Studies of high-pressure material behavior typically need to strike a balance between accessing the most extreme conditions and precise control of conditions, a choice that often limitsl the ability to investigate how materials deform when sheared and to find new materials with useful applications. A new study led by CDAC Academic Partner Susannah Dorfman at Michigan State University demonstrates a method for tuning the degree to which a sample is subjected to shear stresses while under simultaneous applied pressure.
The method is based on using a two-layered sample, similar to the bimetallic strip in a mechanical thermostat. When the two attached layers have different physical properties, they will expand or contract to different degrees when the temperature changes, causing the layers to bend together. A thin film (up to several hundred nanometers thick) sample in contact with a thicker substrate can curve enough to result in gigapascals of stress.
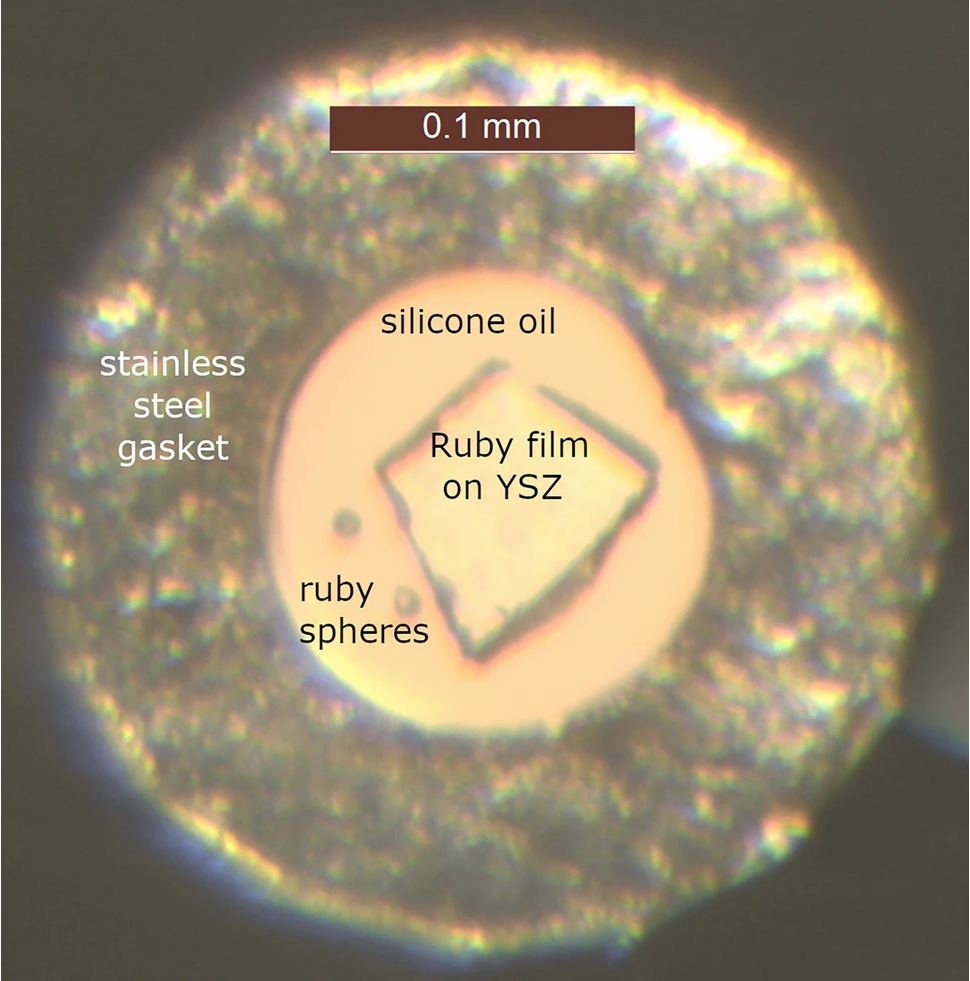
In a previous published work [Journal of Applied Physics 125, 245904 (2019)] graduate student Eric Straley in Dr. Jason Nicholas’ lab at MSU made thin film bilayers using pulsed laser deposition. Results from this work showed that the stress in the film determined by fluorescence spectroscopy was consistent with independent measurement of bending stress, and that a ruby film on a cubic zirconia substrate with contrasting physical properties retains ~1 GPa stress at standard temperature and pressure.
The new study combines these thin film bilayers with the diamond anvil cell, which can generate the highest static stresses possible in a laboratory setting. Again leveraging the strong fluorescence of ruby that is responsible for its characteristic red color, the variation in stress in the thin ruby film is measured as a function of additional confining stress. Measured stresses in a ruby film on a cubic zirconia substrate under compression (Fig. 1) continued to be significantly higher than a ruby on sapphire control sample due to bending of the bilayer. Differences in compressibility between the two layers also generated increasing amounts of bending stress in the sample, reaching as much as ~4 GPa when the confining pressure was 10 GPa.
The thin film combined with the diamond anvil cell method retains the advantages of the diamond anvil cell technique, including optical access to measurements and potential to reach hundreds of GPa pressures (millions of atmospheres), applicable to planetary cores and large explosive impacts. Future work using different materials may continue to tune stresses and useful properties in thin films over a wide range of conditions.
Co-author and former CDAC graduate student Ben Brugman is now a postdoctoral researcher at Arizona State University; Mingda Lv is now a postdoctoral researcher at HPCAT, and Samantha Theuer and Bella Arroyo were undergraduate participants in Professor Dorfman’s laboratory when this work was carried out.
Dorfman, S. M., S. Najiba, B. Arroyo, S. Theuer, M. Lv and B. L. Brugman, Control of deviatoric stress in the diamond anvil cell through thermal expansion mismatch in thin films. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals 49, 16 (2022).
========================================================================================
Expanding the Potential of High-Temperature Superconductivity
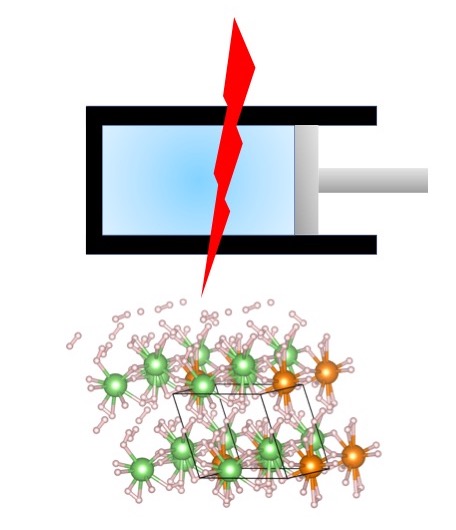
Electrochemical potential and applied pressure have each been used extensively to prepare new materials, such as pure aluminum (electrochemistry) and synthetic diamond (applied pressure). However, these two fundamentally important approaches to chemical synthesis have not been combined, in part due to the difficulties of designing an apparatus that will perform electrochemistry inside a diamond anvil cell. If the associated technical challenges could be overcome, the combination of electrochemistry and pressure (Fig. 1) could provide a powerful new method for the exploration of composition space in the effort to design new materials with tailored properties.
Recent evidence for room-temperature and even “hot” superconductivity in high-pressure hydrides beyond binary compositions suggests that increasing chemical complexity is a key requirement for increasing the superconducting critical temperature (Tc) for these materials. Static pressures near 200 GPa are required to stabilize superconducting superhydrides, and this is currently only achievable using the diamond anvil cell. More importantly, it is often the case that a complex superhydride decomposes into constituent simpler superhydrides even at such high pressures. Many complex superhydrides therefore may never achieve thermodynamic stability by pressure alone, thus preventing thorough investigation of their interesting and important properties.
Following previous work that demonstrated the concept of combing pressure and electrochemistry to synthesize binary superhydrides, a new theoretical study carried out in a collaboration between researchers from Carnegie-Mellon University, Jilin University and the University of Illinois Chicago has recently extended this concept to a ternary hydride system, Li-Mg-H, where Li2MgH16 was previously calculated to have a superconducting critical temperature of ~ 470 K at 250 GPa. However, this complex phase is thermodynamically unstable against binary hydrides.
Combing first-principles calculations, crystal structure prediction and computational thermodynamics, phase diagrams of the Li-Mg-H system can be mapped over the space of composition, pressure and electrochemical conditions (electrode potential and pH), with the one at a fixed Mg/Li ratio between 0 and 0.25. Two ternary Li-Mg superhydrides, Li2MgH16 and Li4MgH24 can be thermodynamically stabilized at suitable negative electrode potentials, if the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) can be kinetically suppressed, which may be achieved by superconcentrated electrolytes or other mechanisms. The ground state of Li2MgH16 undergoes two polymorphic phase transitions at 33 and 160 GPa. The highest pressure phase is superconducting, while the two lower pressure phases are not.
This work shows the great potential of combing pressure and electrochemistry to synthesize novel multi-component superhydrides at low pressures, which may not be achieved even by applying multimegabar pressure alone. In practice, the highest achievable hydrogenation will depend on suppressing HER and on engineering issues like maintaining structural integrity of the highly hydrogenated electrode. Such a vast space of novel phases will provide many exciting opportunities for experimental and further theoretical research.
Guan, P.-W., Y. Sun, R. J. Hemley, H. Liu, Y. Ma, and V. Viswanathan, Low-pressure electrochemical synthesis of complex high-pressure superconducting superhydrides. Physical Review Letters 128, 186001 (2022).
========================================================================================
Eva Zurek Elected to the Chair Line of the APS Division of Computational Physics

CDAC Academic Partner Eva Zurek, Professor of Chemistry at the University at Buffalo, has been elected to the chair line of the American Physical Society’s Division of Computational Physics. Over the next four years, Professor Zurek will serve as Vice Chair, Chair-Elect, Chair, and Past Chair.
The goals of the Computational Physics Division are to “promote research and development in computational physics, enhance the prestige and professional standing of its members, encourage scholarly publication, and promote international cooperation in these activities.”
For more on Professor Zurek’s work, visit her research site.
Congratulations, Eva!
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the 2022 SSAP Symposium

The SSAP Symposium for 2022 was held virtually for the second year in a row on February 15-17. The keynote address was given by Dr. Njema Frazier, who is the Assistant Deputy Administrator for Strategic Partnerships at DOE/NNSA. Dr. Frazier outlined the changes taking place in the NNSA organizational structure that have been implemented in response to the strategic priorities articulated by the new administration.
Overview presentations were provided by all SSAP Grant Holders and Center Directors in the High Energy Density Laser Plasma, National Laser User Facility, Low Energy Nuclear Science, Radiochemistry and Materials Sections. Russell Hemley provided updates CDAC scientific progress and student training activities since the Center’s move to the new host institution, the University of Illinois Chicago.
Breakout sessions held by representatives of the NNSA laboraotories gave students an opportunity to ask questions about postdoctoral research and staff positions, as well as the mission and research culture at each laboratory.
CDAC graduate students presented their research in the poster session. Hannah Bausch, a graduate student in the group of Academic Partner Steven Jacobson at Northwestern University, received a Best Poster Award for her presentation, Shock-Ramp Compression of (Mg,Fe)O on the Z Machine: Preliminary Theory and Application to Ultra-Low Velocity Zones Atop the Core-Mantle Boundary. Hannah’s poster described computational work that is carried out in collaboration with former CDAC student Josh Townsend, now at Sandia National Laboratories.
Next year’s Symposium will be held on February 14-15, 2023 and is tentatively scheduled to be an in-person event at the Buffalo Thunder Hotel and Casino in Albuquerque, NM.
Posters presented at this year’s symposium by CDAC graduate students illustrate the wide range of scientific work in which they are engaged:
Charlie Zoller, University of Illinois – Chicago
Highly Accurate EoS of Statically Compressed H2 – He Mixtures
Roma Ripani, University of Illinois – Chicago
Hydrazine at High Pressures
Allison Pease, Michigan State University
Deformation of Iron Nitrides
Alexander Mark, University of Illinois – Chicago
Structural Studies of Bismuth Based High Temperature Superconductors to Megabar Pressures
Chantelle Kiessner, University of Utah
Strain-Rate Dependence of Texture Evolution in Zircon
Jacob Minnette, University of Tennessee
Radiation Response of Carbide Fuel-Type Materials to SHI Irradiation Across Different Grain Sizes
Brian Blankenau, University of Illinois – Urbana-Champaign
Exploring Pressure and Temperature Induced Martensitic Phase Transformations in Ni2Mn2-xInx Alloys
Hannah Bausch, Northwestern University
Shock-Ramp Compression of (Mg,Fe)O on the Z Machine: Preliminary Theory and Application to Ultra-Low Velocity Zones Atop the Core-Mantle Boundary
========================================================================================
Melting of Iron at Super-Earth Core Conditions
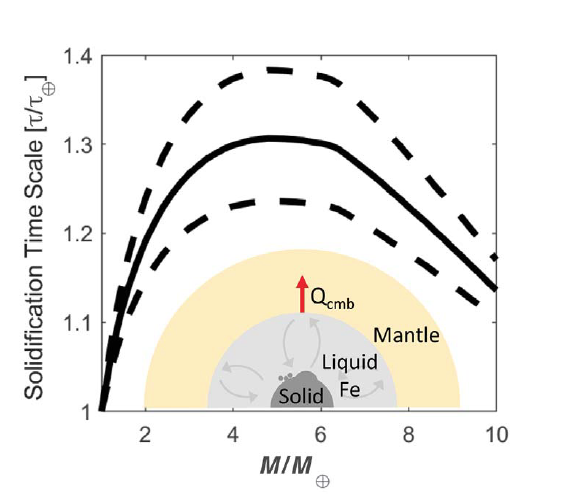
As the number of exoplanets discovered continues to increase, the question of whether they are capable of supporting life has become one of the key scientific questions in Earth and planetary science research today. To understand the dynamics of planetary interiors that may be similar to that of Earth, an understanding of the melting behavior of iron at the pressures of “Super Earth” planetary bodies can provide crucial constraints on accretion, differentiation, and dynamics.
As part of the Discovery Science Program at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Staff Scientist Richard Kraus and CDAC Director Russell Hemley and have recently led a dynamic compression study in which iron was compressed to terapascal pressures, nearly three times that of Earth’s core, to simulate the conditions of Super Earth cores. As the world’s most powerful laser, NIF has the capability to produce conditions unreachable with static compression or with other types of dynamic compression techniques.
Simultaneous measurements of X-ray diffraction during compression reveal that, with decreasing entropy at a constant peak pressure (as would be the case for a planet during cooling), iron undergoes a transition from a completely liquid state, to a mixed hcp-liquid, and finally to solid hcp state. This sequence of phase transformations is observed up to 1000 GPa, or 1 Terapascal (TPa), and constrains the melting behavior of iron up to four times greater pressure than previous measurements.
This work has important implications for models of solidification of planetary cores (Fig. 1) and the formation and duration of planetary dynamos. In the latter case, observations from the current work lead to the assertion that super Earth-sized planets should have a longer period during which conditions favoring habitability are possible due to magnetic shielding of cosmic radiation.
Kraus, R. G., R. J. Hemley, et al., Measuring the melting curve of iron at super-Earth core conditions. Science 375, 202-205 (2022).
For a commentary on this work from Jung-Fu Lin, a former CDAC Research Scientist and current Professor in the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Texas at Austin, see his Perspective.
Perspectives Article in Physics Today
========================================================================================
Synthesis of Superhydrides Using Pressure and Electrochemistry
Superhydrides of main group or rare earth elements have received a great deal of attention in recent years due to the prediction and observation of superconductivity at our near room temperature at pressures approaching two megabars (200 GPa). Compounds containing a large excess of hydrogen, such as LaH10, are a realization of the prediction that a metal hydride could exert a chemical “pecompression” and promote metallization and perhaps also superconductivity at pressures below the that required for the transition of pure hydrogen to the monoatomic, metallic, superconducting state.
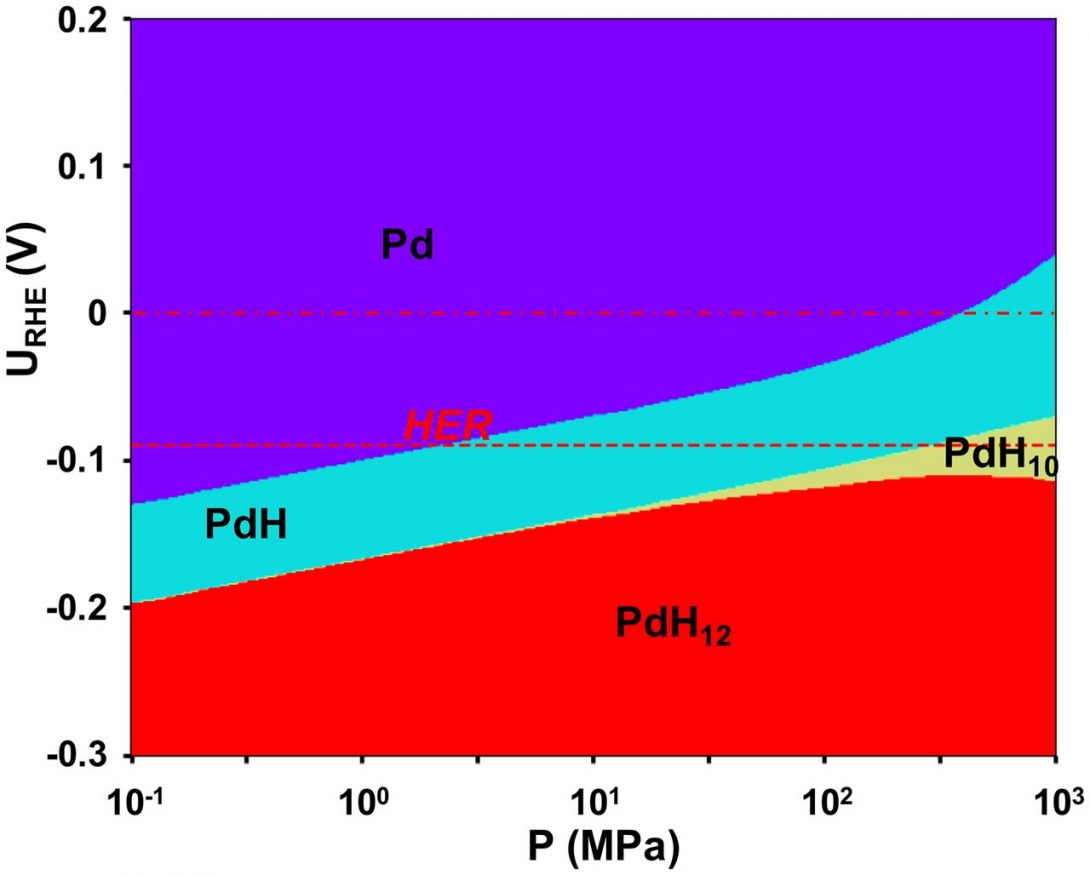
Such experiments are especially challenging due to the synthesis pressures required, which approach the pressures at which the onset of superconductivity is observed. In new theoretical/computational work, CDAC Director Russell Hemley (University of Illinois – Chicago) and CDAC collaborators at Carnegie-Mellon University propose a synthesis method for superhydrides that combines high pressure with an electrochemical potential provided by an electrode inside the pressure cell. The electrode is designed to surpress the evolution of hydrogen and at the same time allow the loading of hydrogen by modulating the activity of mobile protons from the electrolyte.
As an example, the calculated activity required to synthesize palladium hydrides as a function of pressure is illustrated in a Pourbaix diagram (Fig. 1). Although current experimental work has shown that PdH10 would be difficult if not impossible to synthesize even at multimegabar pressures with laser heating, the pressure-potential method suggests that modest pressures of about 0.1- 1.0 GPa would be needed to synthesize this material in an electrochemical environment. Through a judicious choice of electrolyte that could suppress the hydrogen evolution reaction further, PdH10 could be stable at even lower pressures with a more negative electrode potential. This approach may be extended to other superhydride systems, such as La-H, Y-H and Mg-H.
Guan, P.-W., R. J. Hemley and V. Viswanathan, Combining pressure and electrochemistry to synthesize superhydrides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 118, e2110470118 (2021).
========================================================================================
X-ray Diffraction and Equation of State of the C-S-H Room-Temperature Superconductor
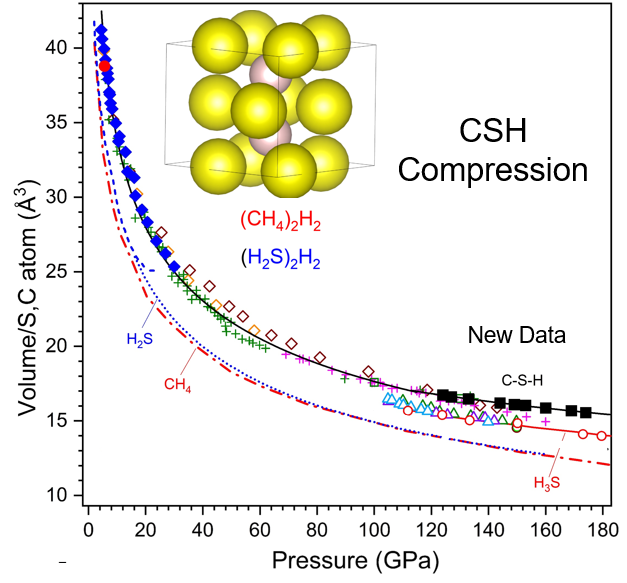
A new paper from groups at UIC, Rochester, HPCAT and GSECARS reports an x-ray diffraction study of the recently discovered carbonaceous sulfur hydride (C–S–H) room-temperature superconductor. The study indicates that the structure of the C-S-H superconductor is derived from the structures of previously established van der Waals compounds found in the H2S–H2 and CH4–H2 systems.
Crystals of the superconducting phase were produced by a photochemical synthesis technique, and yielded a superconducting critical temperature (Tc) of 288 K at 267 GPa. For this work, x-ray diffraction patterns measured from 124 to 178 GPa (i.e. within the pressure range of the superconducting phase), are consistent with an orthorhombic structure derived from the Al2Cu-type determined for (H2S)2H2 and (CH4)2H2 but differ from those predicted and observed for the H3S system, which also exhibits a very high Tc at these pressures.
The formation and stability of the C–S–H compound may be understood in terms of the close similarity in effective volumes of the H2S and CH4 components (Fig. 1) Denser carbon-bearing S–H phases are predicted to form at higher pressures, and the current results provide a critical starting point for understanding the very high superconducting transition temperatures found in the C–S–H system at megabar pressures.
Lamichhane, A., et al., X-ray diffraction and equation of state of the C–S–H room-temperature superconductor. Journal of Chemical Physics 155, 114703 (2021).
========================================================================================
New Structural Motifs in Boron at Megabar Pressures
Apart from its fascinating crystal structures and their structural chemistry, the high pressure behavior of boron is of critical importance in high-energy density research, particularly due to its role as an ablator in inertial confinement fusion experiments.
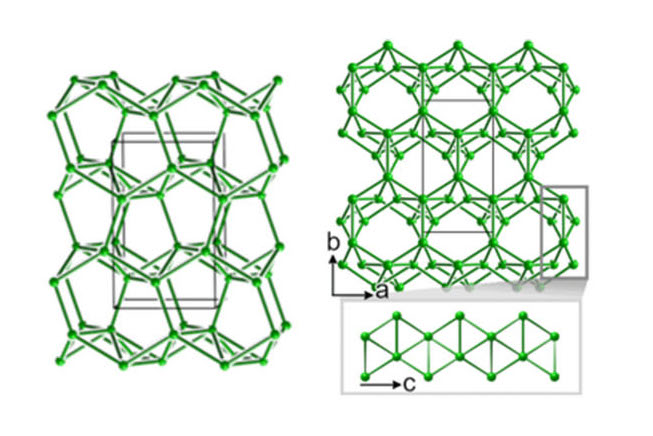
New theoretical and computational results from a collaboration led by CDAC Postdoctoral Associate Katerina Hilleke and CDAC Academic Partner Eva Zurek at the University at Buffalo, and including colleagues at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the University of Rochester/Laboratory for Laser Energetics, sheds new light on the behavior of boron at megabar pressures, and provides structural models for understanding the stability of several predicted high-pressure polymorphs containing unique structural motifs.
Using evolutionary algorithm routines implemented in the XtalOpt code, the group predicts several metastable phases of boron that are dynamically stable at 100 GPa, and which can be sorted into two different types. One is based on the structure of α-Ga, and the other consists of channels along the c direction of a monoclinic lattice (Fig. 1). In addition, two intergrowth structures are predicted that are comprised of both a-Ga and channel-based structural units. These phases contain a combination of 2 center – 2 electron, 3 center – 2 electron and 4-center – 2 electron boding motifs, showing that not only are the complex structural features of α-B12 retained at high pressures, but new motifs are generated.
Several of the structures predicted in this work are calculated to be metastable at ambient pressure. With Vickers hardnesses in the range of 36 GPa, these phases, if they could be synthesized by a high P-T route and quenched, have the potential to be useful in a variety of practical applications.
Hilleke, K. P., et al., Structural motifs and bonding in two families of boron structures predicted at megabar pressures. Physical Review Materials 5, 053605 (2021).
========================================================================================
Novel Li-F-H Compounds
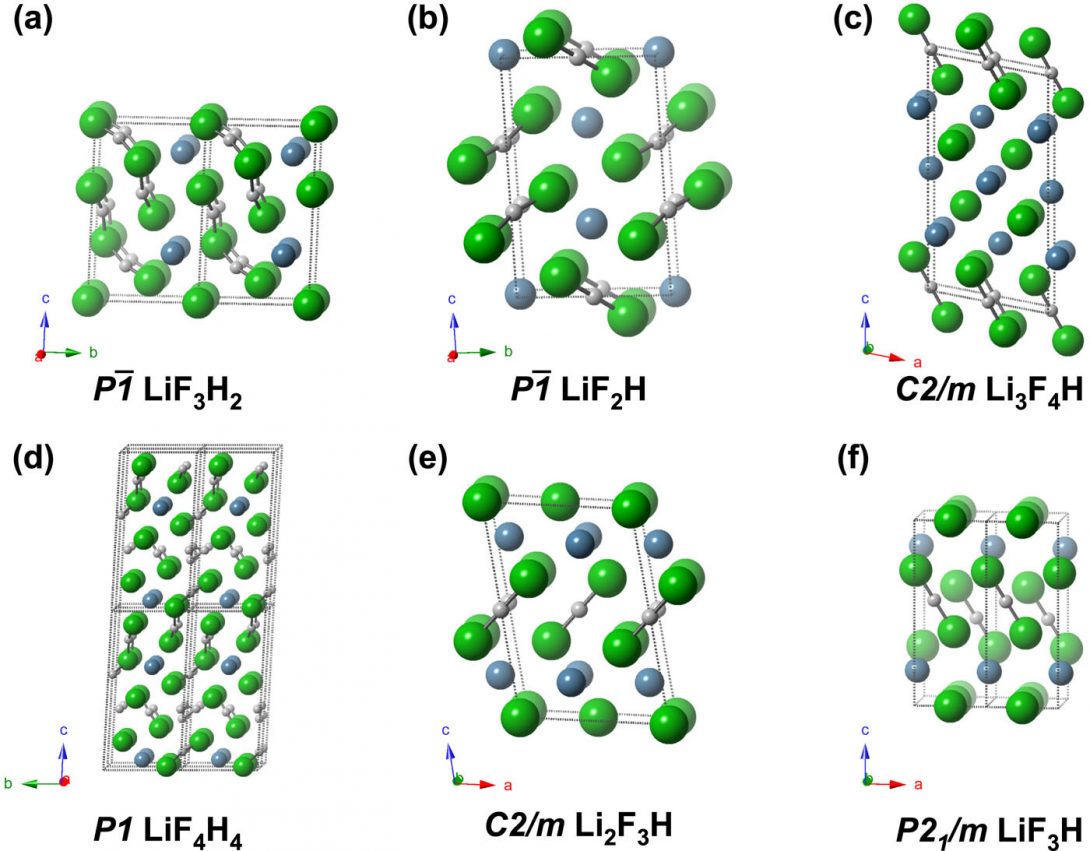
A new CDAC paper from the groups at Buffalo, UIC, and LLNL reports predictions of new pressure-induced chemistry between LiF and hydrogen, with results that have implications for dynamic compression experiments.
Lithium fluoride is a common window in shock compression experiments, and pressure-induced chemical reactions between hydrogen and LiF windows in dynamic compression experiments near 300 GPa, could affect the interpretation of the results. Given the propensity for formation of stable and metastable ternary hydrides under pressure, crystal structure prediction techniques were applied to study the Li-F-H system to multimegabar pressures. Phase diagrams of the elemental (Li, H, and F) and binary (Li-H, H-F, and Li-F,) systems have been studied computationally corresponding to pressures up to 300 GPa, and these results have provided a well-established starting point for exploration of potential high pressure phases in the ternary system.
Evolutionary crystal structure prediction techniques were used evaluate ground state structures containing the elements Li, F, and H at elevated pressures. None of the structures found suggest compound formation in NIF experiments from the combination of LiF and hydrogen isotopes. A number of intriguing metastable phases, however, are predicted that could potentially be synthesized. Common structural motifs present in these phases include HnFn+1– anions of various lengths, and Li+ counter-cations. Most of these crystalline phases are predicted to be wide-gap insulators, with the exception of LiF3H, which calculations predict to be metallic and superconducting below 0.1 K. Li3F4H is found to be thermodynamically and dynamically stable at atmospheric pressure.
Exploratory calculations on the Li3F4H composition predict a structure that contains bent and asymmetric bifluoride anions, as well as infinite HF chains with nearly equal bond lengths, whose enthalpy lies 21.7 meV/atom above the convex hull. The fact that Li3F4H is predicted to be thermodynamically and dynamically stable at ambient pressure, suggests that other Li-F-H compounds with unique HnFn+1-type compositions could also be synthesized and stabilized at ambient conditions (Fig. 1).
These studies provide the basis for future work exploring the finite temperature stability of Li-F-H phases, with the inclusion of anharmonic effects, which are known to be important for light element systems, especially at high pressures.
Bi, T. , A. Shamp, T. Terpstra. R. J. Hemley and E. Zurek, The Li-F-H ternary system at high pressures. Journal of Chemical Physics 154, 124709 (2021).
========================================================================================
CDAC Science at the 2021 SSAP Symposium

The 2021 Stewardship Science Academic Programs (SSAP) Symposium was held in virtual mode from February 16th through the 18th. Principal Investigators for SSAP grants and centers provided updates on their activities through oral presentations, while students supported by SSAP grants and centers also presented their posters this year in five-minute video segments.
The Keynote Address for this year’s symposium was presented by Dr. Mark Anderson, who is the Assistant Deputy Administrator in the Office of Research, Development, Test and Evaluation at DOE/NNSA. Dr. Anderson outlined recent progress in the area of stewardship science, along with scientific and technical challenges that lie ahead, as well as plans for the future, particularly in the development of new experimental and computational capabilities. He emphasized the wide and continuously growing range of opportunities available within the NNSA laboratory complex for scientists, engineers, and other technical professionals.
CDAC was once again well represented at the SSAP Symposium this year. Eleven posters were presented by Center graduate students and represented the Academic Partner groups as well as UIC:
Hannah Bausch (Northwestern) : Origin of the ultra-low velocity zones atop Earth’s core-mantle boundary: Shock-ramp compression of iron-rich (Mg,Fe)O
Brian Blankenau (Illinois/Urbana-Champaign) : First-principles description of the Martensitic phase transformation in Ni2FeGa
Samantha Couper (Utah) : Variant selection across the cubic/monoclinic phase transition in wüstite
Zach Chaney (Tennessee) : Effects on oxidation of zirconium carbide induced by dense electronic excitation
Adam Denchfield (Illinois/Chicago) : Role of zero-point motion in phase transitions of hydrides
John Hirtz (Tennessee) : Solids at extreme conditions: Coupling high pressure with ion beams
Chantelle Kiessner (Utah) : Investigating impacts with high pressure and temperature experiments
Mingda Lyu (Michigan State) : Spin transitions and compressibility of ε-Fe7N3 and γ’-Fe4N: Implications for iron in terrestrial planet cores
Alexander Mark (Illinois/Chicago) : Compression of BSCCO to megabar pressures
Allison Pease (Michigan State) : Deformation of iron nitrides under uniaxial compression to 55 GPa
Charlie Zoller (Illinois/Chicago) : Static pressure-volume equation of state of helium-hydrogen mixtures
Presentations from this year’s symposium will be available on the 2021 SSAP Symposium website. Next year’s SSAP Symposium is planned for February 2022 at the Buffalo Thunder Hotel in Santa Fe, NM.
========================================================================================
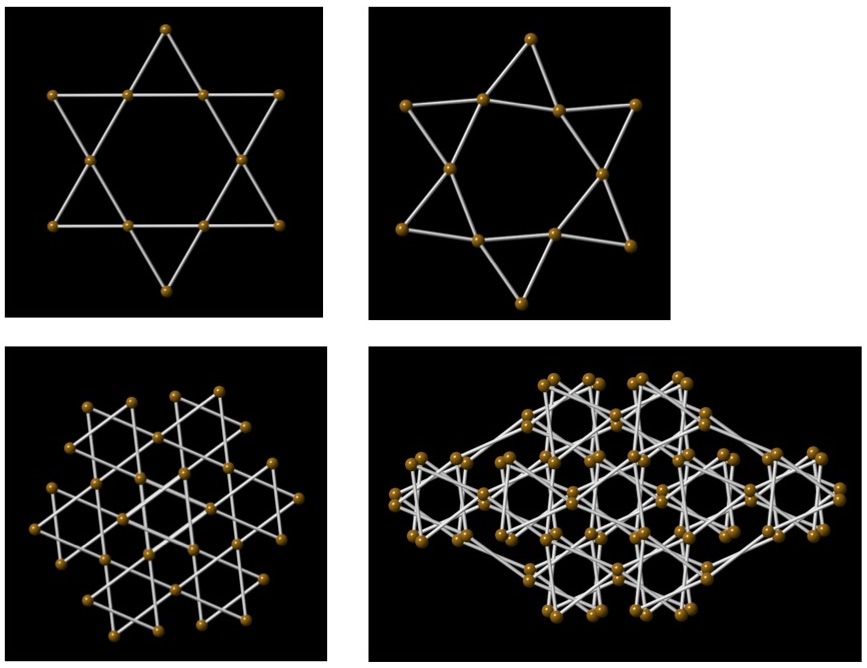
New Capabilities of the XtalOpt Evolutionary Algorithm Code
The expanding research field that is concerned with the a priori prediction and design of materials has led to successful syntheses of phases that were first proposed in theoretical calculations, including the fascinating Fm-3m LaH10 phase, which is consistent with a compound with measured Tc values up to 280 K at 200 GPa. With advances in materials synthesis, computational techniques such as the XtalOpt evolutionary algorithm,designed to predict novel and intriguing structures, have similarly become more adept. New work in the group of CDAC Academic Partner Eva Zurek at the University at Buffalo has resulted in the implementation of new structure prediction tools in the XtalOpt evolutionary algorithm for crystal structure prediction. Forthcoming papers from the Zurek group detail the use of the XtalOpt methodology to determine stable structures at high pressure in the boron and Li-H-F systems.
XtalOpt starts with an initial set of randomly generated structures, which are encouraged towards local order using the newly implemented mitosis and randSpg techniques, respectively breaking down large unit cells into supercells of smaller identical components or enforcing user-defined space groups. Increased local order speeds convergence towards low-enthalpy structures, while the search can be further tailored by the imposition of custom interatomic distance cutoffs and including molecular units in the initial geometries. A search can consider multiple formula units of a given stoichiometry at once, with the user choosing whether and when to allow crossovers between structures with different numbers of formula units. Duplicate structures are removed after detection with the XtalComp algorithm, which directly maps structures onto one another following reduction into a standard orientation.
Finally, stable and superhard materials can be directly targeted, with hardness values calculated by a machine learning model based on the Automatic FLOW (AFLOW) database, which is incorporated into a modified fitness function used to select structures for further procreation. Several new metastable and superhard allotropes of carbon have been identified using this method. All of the search options, along with the progress of the search, can be monitored on-the-fly via a GUI implementation, which shows lists of enthalpies and space groups as well as plots of enthalpy against the generations of structures.
Falls, Z. et al., The XtalOpt evolutionary algorithm for crystal structure prediction. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 125, 1601-1620 (2021).
========================================================================================
Collapse of Magnetic Order in Jarosite
The availability of synchrotron x-ray diffraction, x-ray spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy has enabled numerous advances in the physics of materials at extreme conditions, and the physics of materials with correlated electrons and their behavior at high pressure has been an ongoing area of emphasis. Recently, the Jacobsen group at Northwestern used multiple synchrotron techniques in a study of the frustrated antiferromagnetic material jarosite, KFe3(OH)6(SO4)2. The work combined results from x-ray diffraction and x-ray emission spectroscopy at the HPCAT sector at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory, synchrotron Mössbauer spectroscopy at APS Sector 3, and synchrotron IR spectroscopy at the Frontier Infrared Spectroscopy facility at NSLS-II, Brookhaven National Laboratory. At approximately 45 GPa, the Kagomé net of Fe3+ centers undergoes a collapse of magnetic order, accommodated by the formation of an unusual twisted net in which the triangular geometry of the equilateral triangles of Fe3+ ions is preserved (Fig. 1).
Klein, R. A. et al., Collapse of magnetic order in jarosite. Physical Review Letters 125, 077202 (2020).
========================================================================================
Diamond Encapsulated Silicon Optical Fibers
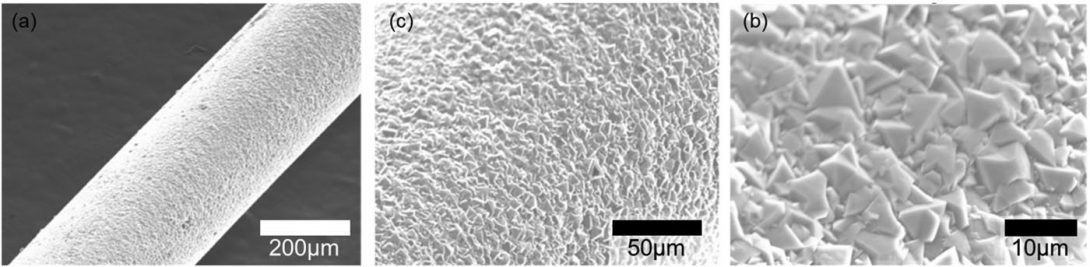
The growth of single-crystal diamond by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) has been a long-standing research direction within the CDAC scientific program. These studies have included the development of CVD chamber technologies as well as the optimization of diamond growth chemistry and the analysis of the enhanced strength and toughness of CVD diamond as compared the natural material. In a recent outgrowth of these studies, a collaboration between Penn State University and CDAC has resulted in the first silicon optical fibers encapsulated by diamond grown by CVD methods (Fig. 1). These fibers, which have a homogeneous diamond morphology over their entire length, have been shown to guide infrared light, and may provide significant enhancements in remote sensing and structural monitoring in extreme environments or when probing for chemical signatures at mid-infrared wavelengths.
Hendrickson, A.T. et al., Diamond Encapsulated Silicon Optical Fibers Synthesized by Chemical Vapor Deposition. AIP Advances 10, 095009 (2020).
========================================================================================